Growth in Telehealth Use Post-COVID-19 Is Here To Stay
Telehealth is a growing part of health care post-COVID-19, with physicians and patients discovering the many ways it can improve access to care.

In the early days of the COVID-19 Pandemic, telehealth use surged, with the number of “virtual” office visits and outpatient care estimated to be 78 times higher in early April 2020 vs. February of that year.* This was driven largely by the temporary closures of most medical offices for any purposes other than COVID or emergencies. And for some time, many patients were hesitant to go for in-person office visits and risk exposure to COVID in a waiting room.
While utilization of telehealth has not remained at such dramatically elevated levels, it has stabilized at a rate 38 times higher than before the pandemic, with an estimated 13 – 17% of visits occurring virtually. While this rate can depend on a number of factors, including medical specialty, adoption of technology, and more, the clear message is that telehealth will be a part of medical care post-COVID-19.
Convenience
Consider a typical doctor appointment, which generally involves a patient driving to the office or medical facility, parking, checking-in, waiting to see the doctor, and then the actual visit, which may only last for only 15 to 30 minutes. In other words, the travel to and from the doctor appointment often lasts longer than the actual appointment itself!
While most patients accepted this process as an inevitable part of seeing their doctor, the use of telehealth during COVID-19 showed many that there is a different way. Instead of driving and waiting, in many cases patients could log on to their computers and connect via video with their doctor. They could describe their symptoms, ask questions, and perhaps even “show” their doctor a cut or rash for examination.
Access to Care
Many patients continue to use telehealth for its convenience, but for others, in remote areas or with limited mobility or access to transportation, telehealth may be their only real access to care.
Across the country, many patients are not in close proximity to medical facilities. This can mean hours-long drives each way when they are in need of health care. For those with chronic conditions, this situation is exacerbated as they frequently need care and may not have reliable access to transportation. This can lead to symptoms or conditions being ignored and worsening.
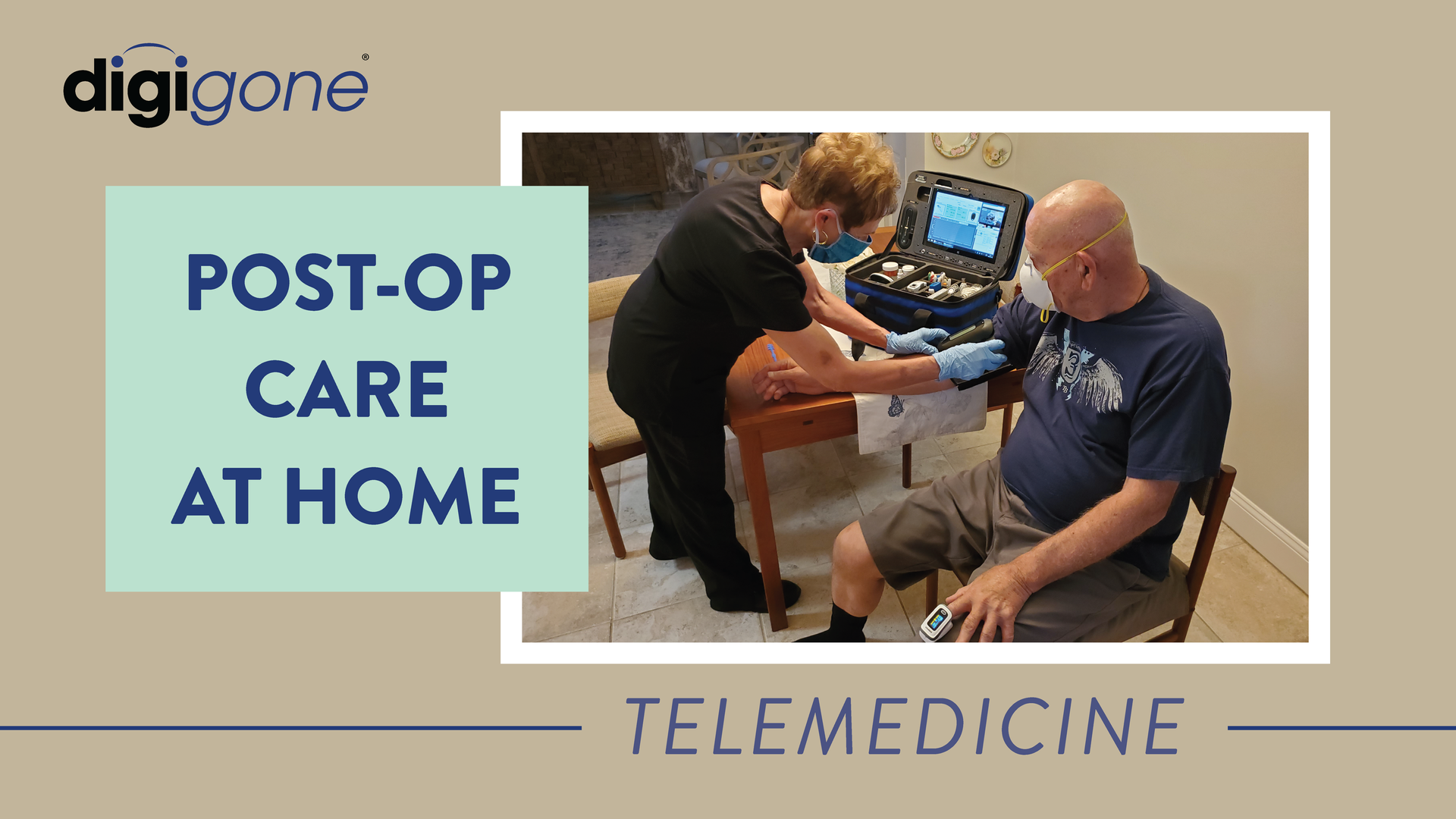
Telehealth can help provide solutions to these challenges. For simple consultations, patients can use video conferencing to check-in with their doctor, monitor treatment and more. For more involved care, home health aides or certified nursing assistants can visit the homes of patients, and using a telemedicine kit with diagnostic tools, take vitals, examine the patients, and share this information with doctors or specialists at any medical facility, no matter how far away.
Effective Option
The initial surge in the use of teleheath may have been driven by the challenges caused by COVID and related closures, but patients continue to use telehealth because it can be an effective option.
Certain medical specialties, such as mental health, have had particularly high telehealth adoption rates (50%) and patients have reported satisfaction and their intention to continue using telehealth going forward. In addition, a majority of physicians view telehealth more favorably now than they did before COVID-19.*
Cost Savings
As the cost of health care continues to increase, many look to telehealth as an opportunity for cost savings. Some possible savings are straightforward: if a trip to the emergency room can be avoided and a patient can instead be diagnosed and a course of treatment determined using telehealth, the savings can equal hundreds or even thousands of dollars.
Other scenarios for cost savings are more complex. Typically a doctor or medical office will have to invest in tools, training and technology to provide telehealth. This can come in the form of video conferencing software, cameras, telemedicine kits and more. To maximize this investment, the doctor or medical office will need to have a strategy in place to help patients understand how and when they can use telehealth services effectively.
What Will Telehealth Look Like?
Telehealth can be used across multiple settings for different purposes. In some cases, all that will be needed is for each participant – doctor and patient – to have a computer, tablet or phone for a video call. But there are certain limitations to the effectiveness of a telehealth visit using only a home computer and camera. The doctor doesn’t have the tools that they would typically use to collect vitals and other information from the patient, making diagnosis of more complex symptoms difficult via telehealth. To be effective in more settings, additional tools are needed.
An important component in effective telemedicine is having a kit with the necessary tools that allow doctors to diagnose and treat patients remotely.
About DigiGone
DigiGone® develops remote communication and medical care solutions, including telemedicine kits and service, which provide our customers with the ability to connect virtually with medical professionals wherever they are via live, encrypted videoconferencing.
*McKinsey & Company, Telehealth: A quarter-trillion-dollar post-COVID-19 reality? (July, 2021)